Try doing this, create an HTML file index.html file and add the following line,
<p>தமிழ்</p>Open the file in your browser and see. This is what I got,
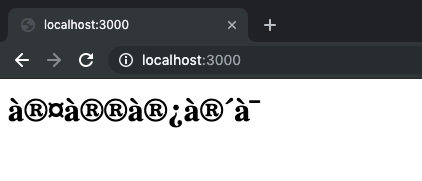
what the hell
Depending on your system and OS you might see the actual Tamil font. If you're not able to see it, then it can be fixed by adding theUTF-8 charset.
<meta charset="UTF-8" /><p>தமிழ்</p>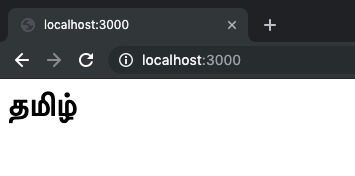
Worked 🎉
What happens is once the browser knows that this is a UTF-8 Unicode Type character, it finds the font that matches the content and displays it.
In my case, it is Times font that came with Mac OS that gets selected as the default font to show, if I'm on Windows it would probably be Latha or Nirmala UI as the font family that the browser selects.
The problem with browser selecting fonts
It's not standard across devices, one OS will show the font as one type and other will do it differently making your styles unreliable.
And some systems will not have Tamil fonts installed in them, Android didn't ship with Tamil fonts until the release of Android 4 and many other devices like the Kindle still doesn't have Tamil fonts in their system.
The Fallback method
The obvious solution for using Tamil fonts on all systems is using the fallback method. So what is the fallback method? Well consider the following style,
body { font-family: Roboto, Arial, sans-serif;}In this style, if you didn't import any fonts on your webpage, your browser will look for the font Roboto first in your system.
If it finds Roboto installed on your system it will display your page in that font otherwise it will move on to searching for Arial and if it can't find that as well, then it will move on to the default sans-serif font in your system. This is the fallback method. If one font isn't available then it immediately moves to the next font in the list.
Remember that this method heavily depends on the fonts being installed on the user's device (unless you import the font), for example, all Android devices over version 4 will always have Roboto font inbuilt so it will be displayed but iOS doesn't have Roboto so it will move on to Arial.
By using this method, let's set a font family for Tamil,
body { font-family: 'InaiMathi', 'Tamil Sangam MN', 'Nirmala UI', Latha, Bamini, Roboto, Noto, 'Noto Sans Tamil', sans-serif;}Let's see what happens here,
body { font-family: 'InaiMathi', 'Tamil Sangam MN', /* For iOS 3+ and Mac */ 'Nirmala UI', Latha, /* For Windows */ Bamini, Roboto, /* For Android 4+ */ Noto, 'Noto Sans Tamil', /* For Ubuntu */ sans-serif; /* For Everything else */}These fonts provide fallback depending on the user's device in question which works for most of the devices that everyone uses.
But using all these fonts will make your text on your webpage look different on different devices and operating systems and could make your brand inconsistent. And what if you don't like any of the Tamil fonts listed above? What if you like a specific Tamil font which you want to use?
The Font-Face property
font-face is a CSS property that allows you to load a custom font on a webpage. For example, let's say there is a font called Shruthi Hassan for which you have the woff and woff2 files.
You can include those fonts in your webpage by using,
@font-face { font-family: 'Shruthi Hassan'; src: url('shruthi-hassan.woff2') format('woff2'), url('shruthi-hassan.woff') format('woff');}The above CSS loads the font file in the URL given and you can use to style elements by using,
body { font-family: 'Shruthi Hassan', Arial, sans-serif;}There are lots of file types for fonts such as, .eot, .woff2, .woff, .ttf, .svg. Most modern browsers recognises .woff2 but you can support all old browsers by using,
@font-face { font-family: 'Shruthi Hassan'; src: url('shruthi-hassan.eot'); /* IE9 Compat Modes */ src: url('shruthi-hassan.eot?#iefix') format('embedded-opentype'), /* IE6-IE8 */ url('shruthi-hassan.woff2') format('woff2'), /* Super Modern Browsers */ url('shruthi-hassan.woff') format('woff'), /* Pretty Modern Browsers */ url('shruthi-hassan.ttf') format('truetype'), /* Safari, Android, iOS */ url('shruthi-hassan.svg#svgFontName') format('svg'); /* Legacy iOS */}From CSS Tricks
From Google Fonts
Google fonts also provides some Tamil fonts which you can use for free in your project, for this example let's see a font called Hind Madurai
You can use this font by adding a link tag to your webpage,
<link href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Hind+Madurai&display=swap" rel="stylesheet"/>and use it to style the text by,
body { font-family: 'Hind Madurai', Arial, sans-serif;}That's all.
Well, that's all if you want to use Hind Madurai as the font for the English version of your font too, but if you want to use Hind Madurai only for Tamil text then move on to the next section.
Unicode-range in Font-Face
The unicode-range is a property where you can specify the specific unicode that you want to load from the font file.
A font may have hundreds of unicode characters, a font might even include emoji characters but we don't need all those, so we can specify the font that we are most interested in to the browser by doing something like this,
@font-face { font-family: 'Shruthi Hassan'; src: url('shruthi-hassan.woff2') format('woff2'), url('shruthi-hassan.woff') format('woff'); unicode-range: U+0964-0965, U+0B82-0BFA, U+200C-200D, U+20B9, U+25CC;}The unicode range given above is specific for Tamil characters, by doing this the browser only uses the font for Tamil text and uses a different font for English text.
The font-display property
And finally for some performance, we can add the font-display property to make sure that there is no empty white space when the font is loading. More details here.
@font-face { font-family: 'Shruthi Hassan'; src: url('shruthi-hassan.woff2') format('woff2'), url('shruthi-hassan.woff') format('woff'); unicode-range: U+0964-0965, U+0B82-0BFA, U+200C-200D, U+20B9, U+25CC; font-display: swap;}The font-display: swap; will make sure that the fallback font is used until the Shruthi Hassan is loaded so that the user can start reading the content rather than waiting for the font to download in an empty page.
Wrapping up
This is how the final font-face property looks like,
@font-face { font-family: 'Shruthi Hassan'; src: url('/fonts/shruthi-hassan.eot'); src: local('Shruthi Hassan'), local('Shruthi-Hassan'), url('/fonts/shruthi-hassan.eot?#iefix') format('embedded-opentype'), url('/fonts/shruthi-hassan.woff2') format('woff2'), url('/fonts/shruthi-hassan.woff') format('woff'), url('/fonts/shruthi-hassan.ttf') format('truetype'); font-weight: normal; font-style: normal; font-display: swap; unicode-range: U+0964-0965, U+0B82-0BFA, U+200C-200D, U+20B9, U+25CC;}Of course, there are even more optimizations that could be done like Subsetting in font files, font face observer, and using service workers to cache the font files but those are fairly advanced concepts, let us know if you are interested in those.
Recommended Reading
