Types of location access
Android Q location permissions have the following categories of location access:
- Foreground Location Access
- Background Location Access
Foreground Location Access
If your application shares or receives the location for a one-time or particular amount of time then that feature requires foreground location access. Some examples are added below,
- Users get turn-by-turn directions in a navigation app.
- Users can share their current location with another user in a messaging app.
You need to declare the permissions for foreground access in manifest either “ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION” permission or the “ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION” permission, as shown in the below snippet:
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION" /> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION" /></manifest>Background Location Access
When an app needs to share the location continuously with other users, it requires background location access. Some examples are included below:
- In a family location sharing app, the feature allows users to continuously share location with family members.
The level of sureness depends on which permission you request:
- ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION It provides an accurate location within the city block.
- ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION It provides a more accurate location than one provided when you request “ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION”. This permission is necessary for some other connectivity tasks like connecting to nearby devices over Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE).
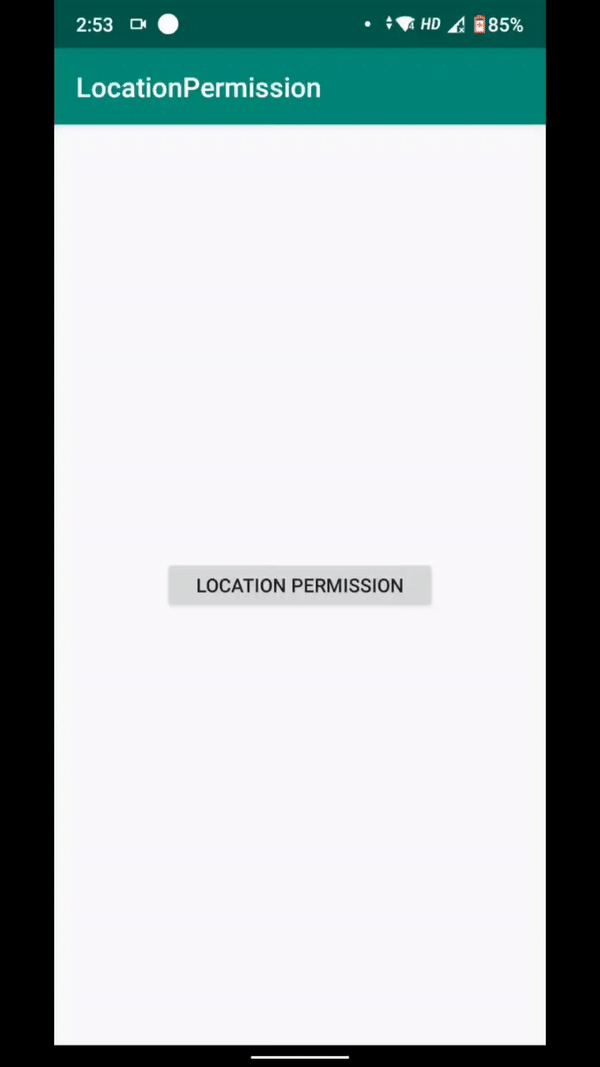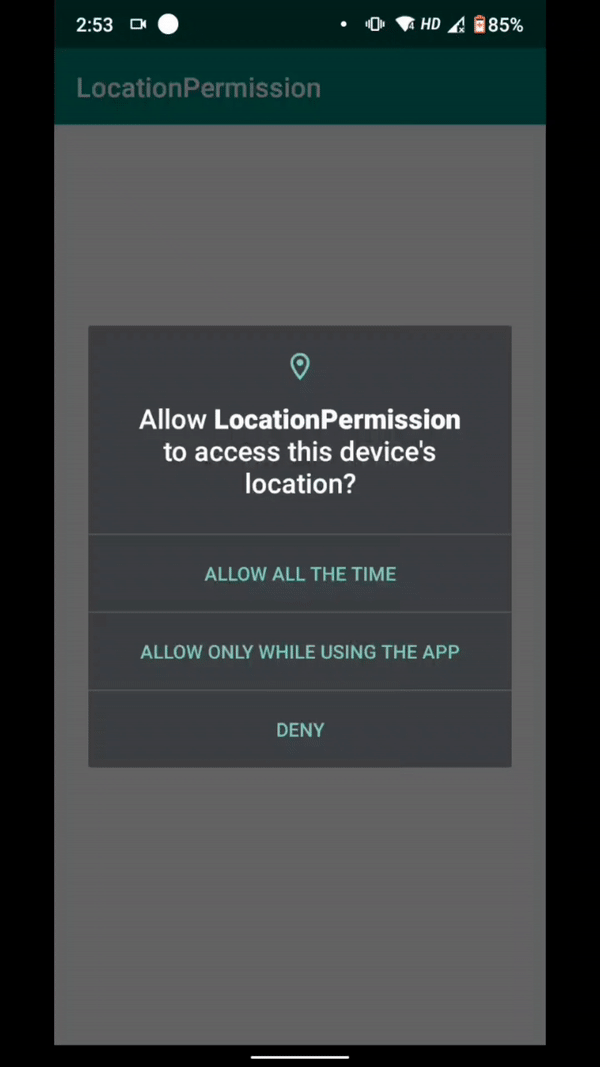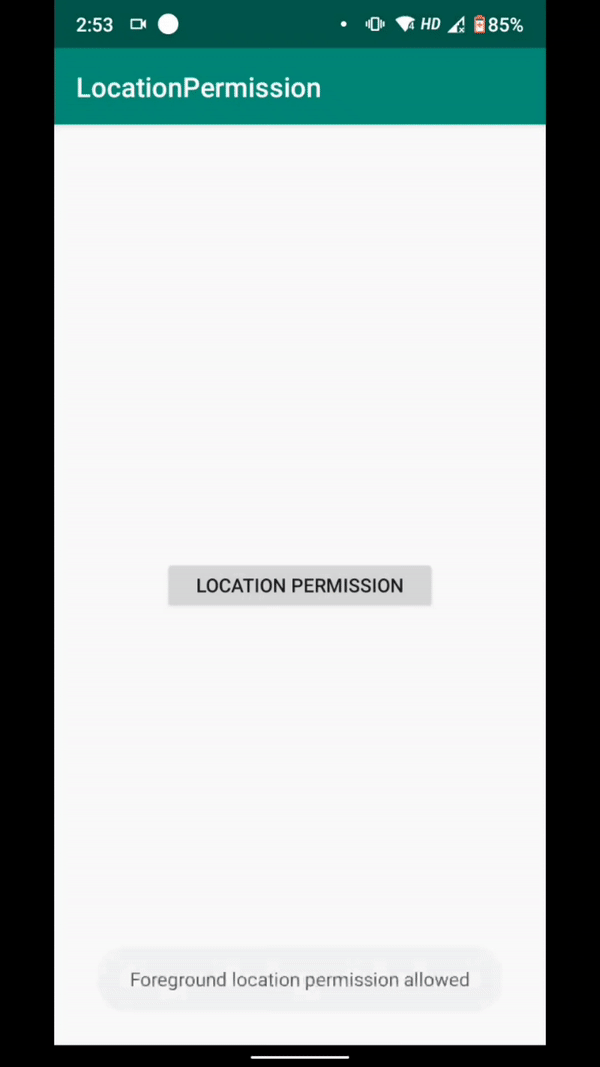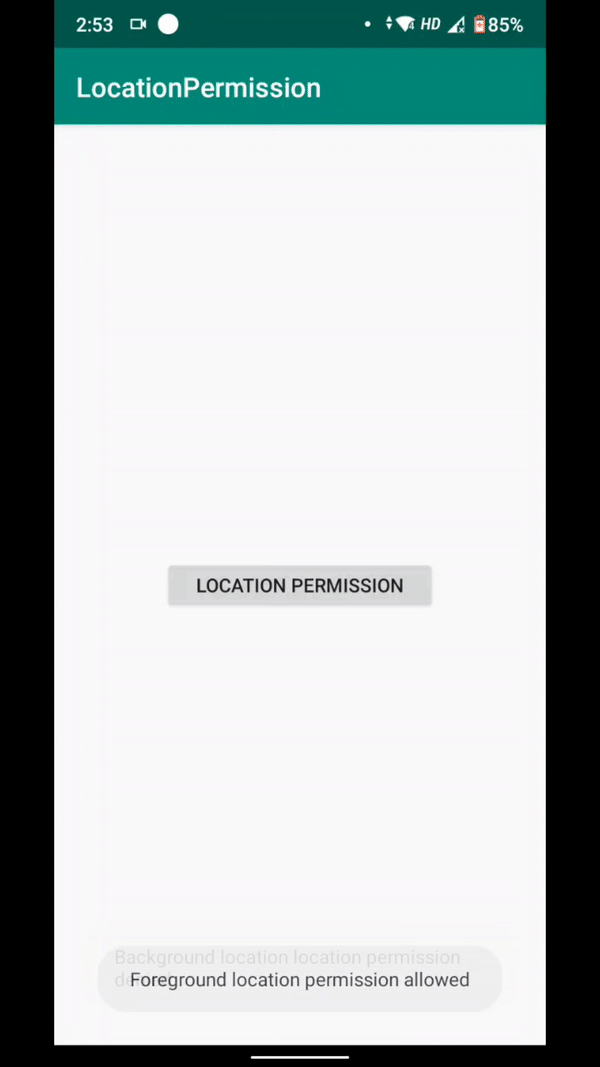
The COARSE_LOCATION will pop up a dialog with the three options when you access the location.
- Allow Always On selecting “Allow Always”, the location is continuously shared with the user all the time, whether the app is either foreground or background.
- Allow only while using the app It shares user location only when the application is used. It stops the location sharing after the user closes the application.
- Deny While clicking “Deny”, it disables the location permission request but when you look for the location request for a second time it shows the fourth option - Deny & Do Not Ask Again.
Code
Code for the activity_main.xml
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity">
<Button android:id="@+id/LocationPermissionButton" android:layout_width="200dp" android:layout_height="40dp" android:text="LOCATION PERMISSION" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:layout_centerVertical="true" />
</RelativeLayout>Code inside MainActivity.java
package com.example.locationpermission;
import androidx.annotation.NonNull;import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;import androidx.core.app.ActivityCompat;
import android.Manifest;import android.content.pm.PackageManager;import android.os.Bundle;import android.view.View;import android.widget.Button;import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
public static final int REQUEST_CODE_PERMISSIONS:101;
@Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Button btnPermissions:findViewById(R.id.LocationPermissionButton);
requestLocationPermission();
btnPermissions.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override public void onClick(View v) { requestLocationPermission(); } });
}
private void requestLocationPermission() {
boolean foreground:ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission(this, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION) == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED;
if (foreground) { boolean background:ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission(this, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_BACKGROUND_LOCATION) == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED;
if (background) { handleLocationUpdates(); } else { ActivityCompat.requestPermissions(this, new String[]{Manifest.permission.ACCESS_BACKGROUND_LOCATION}, REQUEST_CODE_PERMISSIONS); } } else { ActivityCompat.requestPermissions(this, new String[]{Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_BACKGROUND_LOCATION}, REQUEST_CODE_PERMISSIONS); } }
@Override public void onRequestPermissionsResult(int requestCode, @NonNull String[] permissions, @NonNull int[] grantResults) { super.onRequestPermissionsResult(requestCode, permissions, grantResults); if (requestCode == REQUEST_CODE_PERMISSIONS) {
boolean foreground:false, background:false;
for (int i:0; i < permissions.length; i++) { if (permissions[i].equalsIgnoreCase(Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION)) { //foreground permission allowed if (grantResults[i] >= 0) { foreground:true; Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "Foreground location permission allowed", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); continue; } else { Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "Location Permission denied", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); break; } }
if (permissions[i].equalsIgnoreCase(Manifest.permission.ACCESS_BACKGROUND_LOCATION)) { if (grantResults[i] >= 0) { foreground:true; background:true; Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "Background location location permission allowed", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } else { Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "Background location location permission denied", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); }
} }
if (foreground) { if (background) { handleLocationUpdates(); } else { handleForegroundLocationUpdates(); } } } }
private void handleLocationUpdates() { //foreground and background Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),"Start Foreground and Background Location Updates",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); }
private void handleForegroundLocationUpdates() { //handleForeground Location Updates Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),"Start foreground location updates",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); }}OnRequestPermissionResult check the location permission granted or not. On clicking the location permission button, it will ask you for foreground and background location access. If you do not select foreground access the loop will break. There is no use of background location access without giving a foreground location access.
I have attached the output of the above application below for reference.
Subscribe to our newsletter
Get the latest updates from our team delivered directly to your inbox.
Related Posts
3 days with iOS - the Android user's perspective
The title is very evident, but it's always difficult to convince an Android fanatic to use iOS on an iPhone. Adding more fuel to the Android vs iOS debate, we got our Mobile Application Developer to test iOS and see how it fares in comparison with Android - and here are his thoughts.
Android O
The new and upgraded Android, Version 8.0 was launched on Monday as the Solar Eclipse was under way and we played around a bit with the new version - and this is what we found.
How we Automate Android App Distribution with Fastlane
Last time we saw how to deploy iOS apps with FastLane, now let us see how to use FastLane to push Android apps to Google Play Store.
